ETL vs ELT
What are the key differences and benefits? This guide provides definitions and practical advice to help you understand the differences as you evaluate ETL vs ELT for your organization.
ETL vs ELT Guide
ETL vs ELT Overview
The ETL and ELT acronyms both describe processes of cleaning, enriching, and transforming data from a variety of sources before integrating it for use in data analytics, business intelligence and data science.
ETL vs ELT Comparison
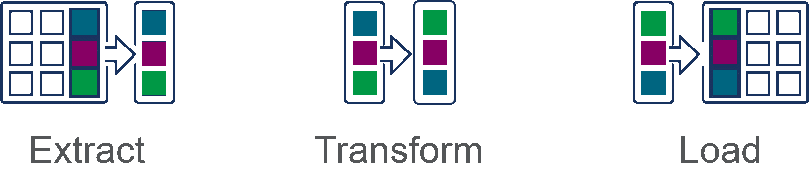
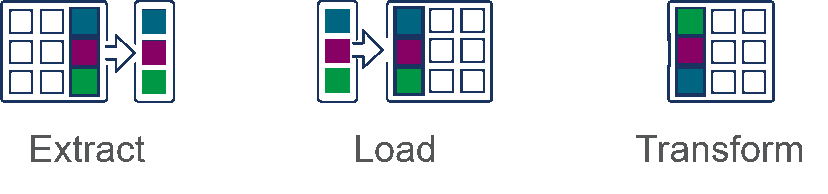
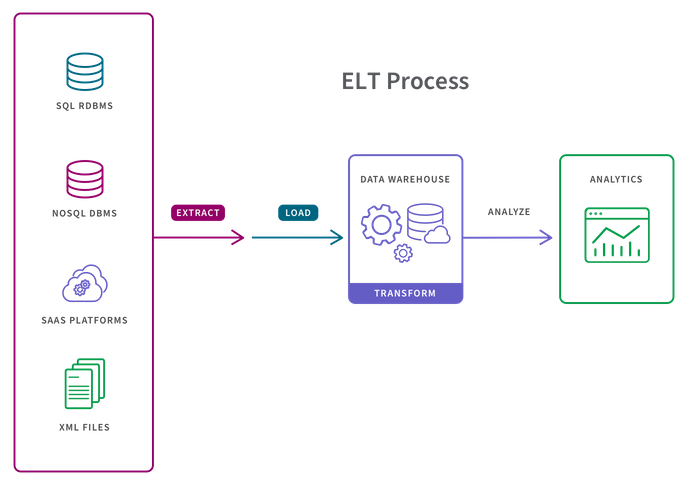
- Extract refers to the process of pulling data from a source such as an SQL or NoSQL database, an XML file or a cloud platform.
- Transform refers to the process of converting the format or structure of a data set to match that of a target system.
- Load refers to the process of placing a data set into a target system.
Here is a side-by-side comparison of the two processes:
In the ETL process, data transformation is performed in a staging area outside of the data warehouse and the entire data must be transformed before loading. As a result, transforming larger data sets can take a long time up front but analysis can take place immediately once the ETL process is complete.
In the ELT process, data transformation is performed on an as-needed basis in the target system itself. As a result, the transformation step takes little time but can slow down the querying and analysis processes if there is not sufficient processing power in the cloud solution.
The ETL process is appropriate for small data sets which require complex transformations. The ELT process is more appropriate for larger, structured and unstructured data sets and when timeliness is important.
The shift from ETL to ELT has been underway for some time.ETL pipelines have long been the standard of data integration since traditionally, the target repository was a data warehouse. But ETL requires expensive hardware and regular IT support and takes longer for ad hoc analysis because the whole process must be repeated for every use case. Further, the ETL process doesn’t support real-time analytics or machine learning projects. These business needs, combined with modern cloud architectures and today’s agile development approaches have accelerated the shift from ETL to ELT.
Latest trend: decoupling the “T” from your monolithic ETL pipeline.Watch this brief video to learn why the market is now shifting from ETL to ELT.
ETL or ELT?
Times are changing. Download the eBook to learn how to choose the right approach for your business, what ELT delivers that ETL can’t, and how to build a real-time data pipeline with ELT.
What is ETL?
ETL is an acronym for “Extract, Transform, and Load” and describes the three stages of the traditional data pipeline. The ETL process is appropriate for small data sets which require complex transformations.
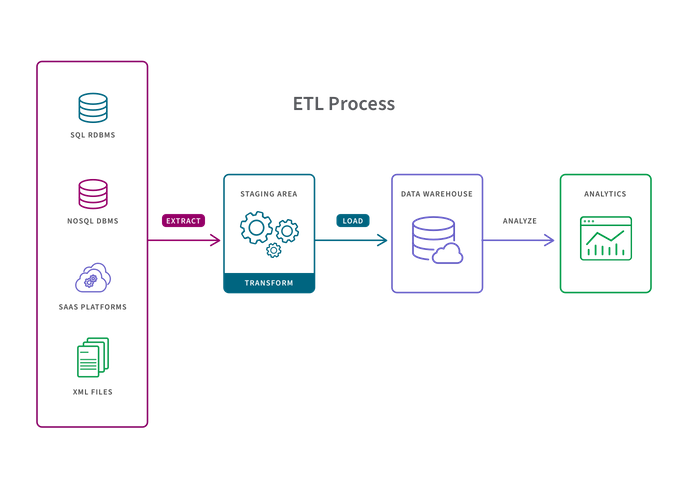
ETL Process
- A predetermined subset of data is extracted from the source.
- Data is transformed in a staging area in some way such as data mapping, applying concatenations or calculations. Transforming the data before it is loaded is necessary to deal with the constraints of traditional data warehouses.
- Data is loaded into the target data warehouse system and is ready to be analyzed by BI tools or data analytics tools.
- Data analysis on a single, pre-defined use case can be slightly more stable and faster with the ETL process given that the data set has already been structured and transformed.
- Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA standards is easier with ETL given that users can omit any sensitive data prior to loading in the target system.
Learn more about the ETL process.
What is ELT?
ELT is an acronym for “Extract, Load, and Transform” and describes the three stages of the modern data pipeline. The ELT process is more cost effective then ETL, is appropriate for larger, structured and unstructured data sets and when timeliness is important.
ELT Process
- All data is extracted from the source.
- All data is immediately loaded into the target system (either a data warehouse, data mart, or data lake). This can include raw, unstructured, semi-structured and structured data types.
- Data is transformed in the target system and is ready to be analyzed by BI tools or data analytics tools
Typically, the target system for ELT is a cloud-based data lake, data mart, data warehouse or data lakehouse. These cloud-based platforms such as Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, Azure Synapse, Databricks and Amazon EMR offer near-unlimited storage and extensive processing power. This allows users to extract and load any and all data they may need in near real time. The cloud platforms transform the data for any BI, analytics, or predictive modeling use case at any time.
Key benefits of ELT- Real-time, flexible data analysis. Users have the flexibility to explore the complete data set, including real-time data, in any direction, without having to wait for IT to extract, transform and load more data.
- Lower cost and lower maintenance. ELT benefits from a robust ecosystem of cloud-based platforms which offer much lower costs and a variety of plan options to store and process data. And, the ELT process typically requires low maintenance given that all data is always available and the transformation process is usually automated and cloud-based.
Learn more about the ELT process.
Comparison Guide: Top Cloud Data Warehouses
ETL vs ELT Comparison Matrix
Many organizations use both the ETL and ELT processes to cover the spectrum of their data pipeline needs. Let’s take a side-by-side look at the pros and cons of ETL vs ELT, and how they can work in tandem to provide a holistic data integration solution for your business.
ETL vs ELT — 10 Key Differences:
| ETL | ELT | |
|---|---|---|
| 1) Support for Data Warehouse |
Yes, ETL is the traditional process for transforming and integrating structured or relational data into a cloud-based or on-premises data warehouse.
|
Yes, ELT is the modern process for transforming and integrating structured or unstructured data into a cloud-based data warehouse.
|
| 2) Support for Data Lake/Mart/Lakehouse |
No, ETL is not an appropriate process for data lakes, data marts or data lakehouses.
|
Yes, the ELT process is tailored to provide a data pipeline for data lakes, data marts or data lakehouses.
|
| 3) Size/type of data set |
ETL is most appropriate for processing smaller, relational data sets which require complex transformations and have been predetermined as being relevant to the analysis goals.
|
ELT can handle any size or type of data and is well suited for processing both structured and unstructured big data. Since the entire data set is loaded, analysts can choose at any time which data to transform and use for analysis.
|
| 4) Implementation |
The ETL process has been around for decades and there is a mature ecosystem of ETL tools and experts readily available to help with implementation.
|
The ELT process is a newer approach and the ecosystem of tools and experts needed to implement it is still growing.
|
| 5) Transformation |
In the ETL process, data transformation is performed in a staging area outside of the data warehouse and the entire data must be transformed before loading. As a result, transforming larger data sets can take a long time up front but analysis can take place immediately once the ETL process is complete.
|
In the ELT process, data transformation is performed on an as-needed basis in the target system itself. As a result, the transformation step takes little time but can slow down the querying and analysis processes if there is not sufficient processing power.
|
| 6. Loading |
The ETL loading step requires data to be loaded into a staging area before being loaded into the target system. This multi-step process takes longer than the ELT process
|
In ELT, the full data set is loaded directly into the target system. Since there is only one step, and it only happens one time, loading in the ELT process is faster than ETL.
|
| 7) Maintenance/Ease of Use |
ETL processes that involve an on-premise server require frequent maintenance by IT given their fixed tables, fixed timelines and the requirement to repeatedly select data to load and transform. Newer automated, cloud-based ETL solutions require little maintenance.
|
The ELT process typically requires low maintenance given that all data is always available and the transformation process is usually automated and cloud-based.
|
| 8) Cost |
ETL can be cost-prohibitive for many small and medium businesses.
|
ELT benefits from a robust ecosystem of cloud-based platforms which offer much lower costs and a variety of plan options to store and process data.
|
| 9) Hardware |
The traditional, on-premises ETL process requires expensive hardware. Newer, cloud-based ETL solutions do not require hardware.
|
Given that the ELT process is inherently cloud-based, no additional hardware is required.
|
| 10) Compliance |
ETL is better suited for compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA standards given that users can omit any sensitive data prior to loading in the target system.
|
ELT carries more risk of exposing private data and not complying with GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA standards given that all data is loaded into the target system.
|
ETL or ELT?
Times are changing. Download the eBook to learn how to choose the right approach for your business, what ELT delivers that ETL can’t, and how to build a real-time data pipeline with ELT.
DataOps for Analytics
Modern data integration delivers real-time, analytics-ready and actionable data to any analytics environment, from Qlik to Tableau, Power BI and beyond.
-

Real-Time Data Streaming (CDC)
Extend enterprise data into live streams to enable modern analytics and microservices with a simple, real-time and universal solution. -

Agile Data Warehouse Automation
Quickly design, build, deploy and manage purpose-built cloud data warehouses without manual coding. -

Managed Data Lake Creation
Automate complex ingestion and transformation processes to provide continuously updated and analytics-ready data lakes. -
Enterprise Data Catalog
Enable analytics across your enterprise with a single, self-service data catalog.

