Self-Service Analytics
What it means, why it matters, and how it works. This guide provides definitions and practical advice to help you understand and practice modern self-service analytics.
Self-Service Analytics Guide
What is Self-Service Analytics?
Self-service analytics provides all users the ability to gain insights from their data, even if they don’t have data or analytics expertise. By giving end users the tools they need to access, visualize and explore data, design dashboards and run reports, IT teams, analysts and data scientists can focus on more critical strategic projects.
Why Self-Service Analytics Matters
Today, businesses are creating and accumulating data at an incredible pace. But making that data easily available to everyday users is one of the biggest hurdles to turning your data into real business value. With self-service data analytics, users can gain insights far more easily and quickly, helping organizations realize the value of their data faster.
Access to self-service analytics tools means business users no longer have to submit a request to IT or an analyst and then wait for answers that may already be outdated. Nor do they have to rely solely on intuition, which could result in poor decisions and costly mistakes.
Instead, self-service analytics facilitates a data-driven culture by giving non-technical users insights at the exact moment they need them, and informed guidance in the form of recommendations. When combined with streamlined business processes and employee training, businesses can also increase data literacy across all business functions.
Benefits of Self-Service Analytics
- Less Reliance on IT: When your IT team spends hours fielding requests for reports, they have less time to work on high-value, long-term projects like data governance and application development. Empowering users to generate their own insights results in fewer IT requests and more technical innovation.
- Insights Without the Wait: Beating out the competition requires agile processes and informed decision-making. With self-service data analytics, business users can spend more time exploring data, weighing insights, and taking decisive action; and spend less time going back and forth with IT on requirements and debating data science vs data analytics.
- Limitless Data Discovery: Every business user has unique needs, so they should be able to slice and dice their data in the way they see fit. But if they’re limited to linear, query-based analysis, their insights are likely to come up short. With Qlik’s Associative Engine, users can explore data freely and uncover insights they never expected.
- Higher Data Literacy: Helping employees grow their analytical skills means giving them the training they need to read, manipulate, analyze and argue with data. That’s the definition of data literacy, and the foundation of a data-driven culture. With a self-service analytics platform, you can increase data literacy across your business.
Modern Analytics Demo Videos
See how to explore information and quickly gain insights.
- Combine data from all your sources
- Dig into KPI visualizations and dashboards
- Get AI-generated insights
Challenges for Self-Service Analytics
- Thin data governance: Balancing the analytics needs of the business with IT’s security requirements is key to building a data-driven culture. But you can only get there with proper data governance. Clean data and standardized data definitions ensure users can confidently make decisions, while permissions and sharing capabilities ensure data access, transparency and security controls.
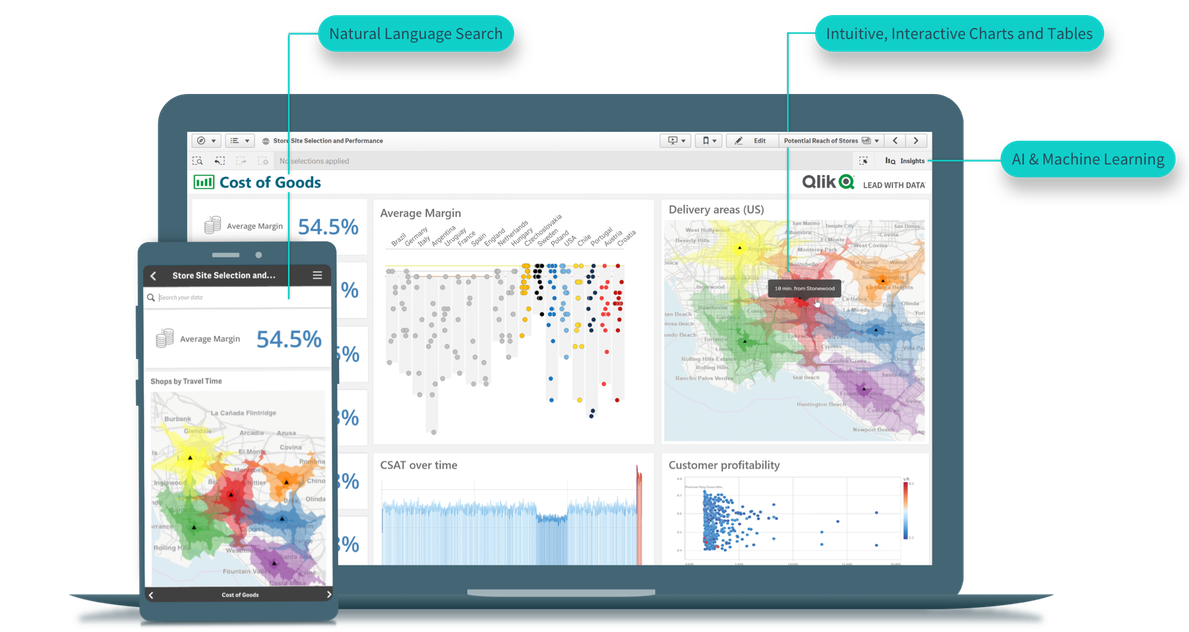
- Limited data exploration: When users have a question about their data, they should have the ability to explore freely and find the answer. Self-service analytics platforms that include capabilities like natural language search, interactive selections and conversational interaction can help workers of any skill level dig deeper in one area, or explore others that pique their curiosity.
- Low levels of data literacy: When business users lack analytics skills, they may be reluctant to dive into their data. In addition to training, a self-service analytics tool that uses AI and machine learning can help users along by automatically providing suggestions and surfacing insights. The right tool can automatically generate and prioritize charts and graphs to help users ascertain the best decisions, faster.
- Barriers to user adoption: If end users have to flip back and forth between applications to gain data insights, there is a greater risk of human error; and many times, they won’t make the extra effort. What’s more, separating insights from daily workflows could impact productivity. By embedding dashboards, charts and tables into applications like ERP, CRM and other systems, workers can make data-driven decisions without leaving their favorite applications.
Find out how Qlik’s Associative Engine makes self-service analytics and BI far more effective.
Self-Service Analytics Best Practices
- Automated Data Pipelines: Self-service analytics begins with a company’s raw data, usually stored in multiple systems. The optimal data integration platform automates the entire process of replicating, ingesting and transforming this data into a data lake or data warehouse, delivering real-time, analytics-ready data streams.
- Enterprise Data Catalog: Enabling users to quickly get the data they need is critical for self-service analytics. A governed data catalog combines all of the company's trusted data, allowing users to easily find, prepare, and publish data sets they can confidently analyze and share.
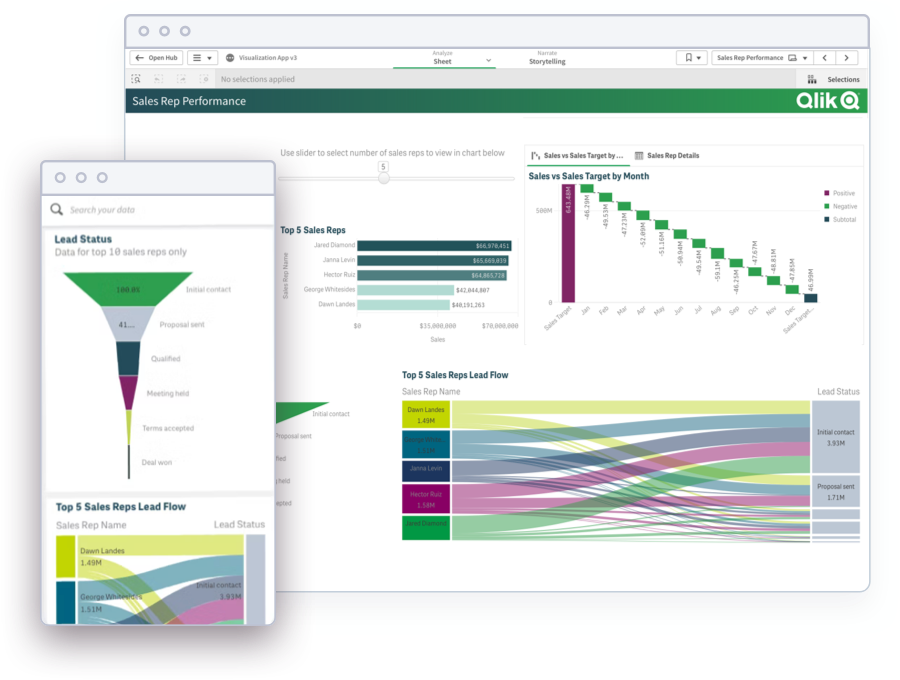
- Data Analytics Platform: A self-service data analytics platform lets business users freely explore and analyze their data with easy-to-use, interactive visualizations, charts and tables. The best self-service technologies also lets users create and share their own analytics apps, dashboards and reports while offering a library of pre-built analytics assets.
- Governance: Underpinning the entire architecture is a governance layer. This includes governance processes, security and compliance, data quality controls, metadata management and data usage audits, ensuring that the right people have access to the right data and data-driven insights come from a single source of truth.

