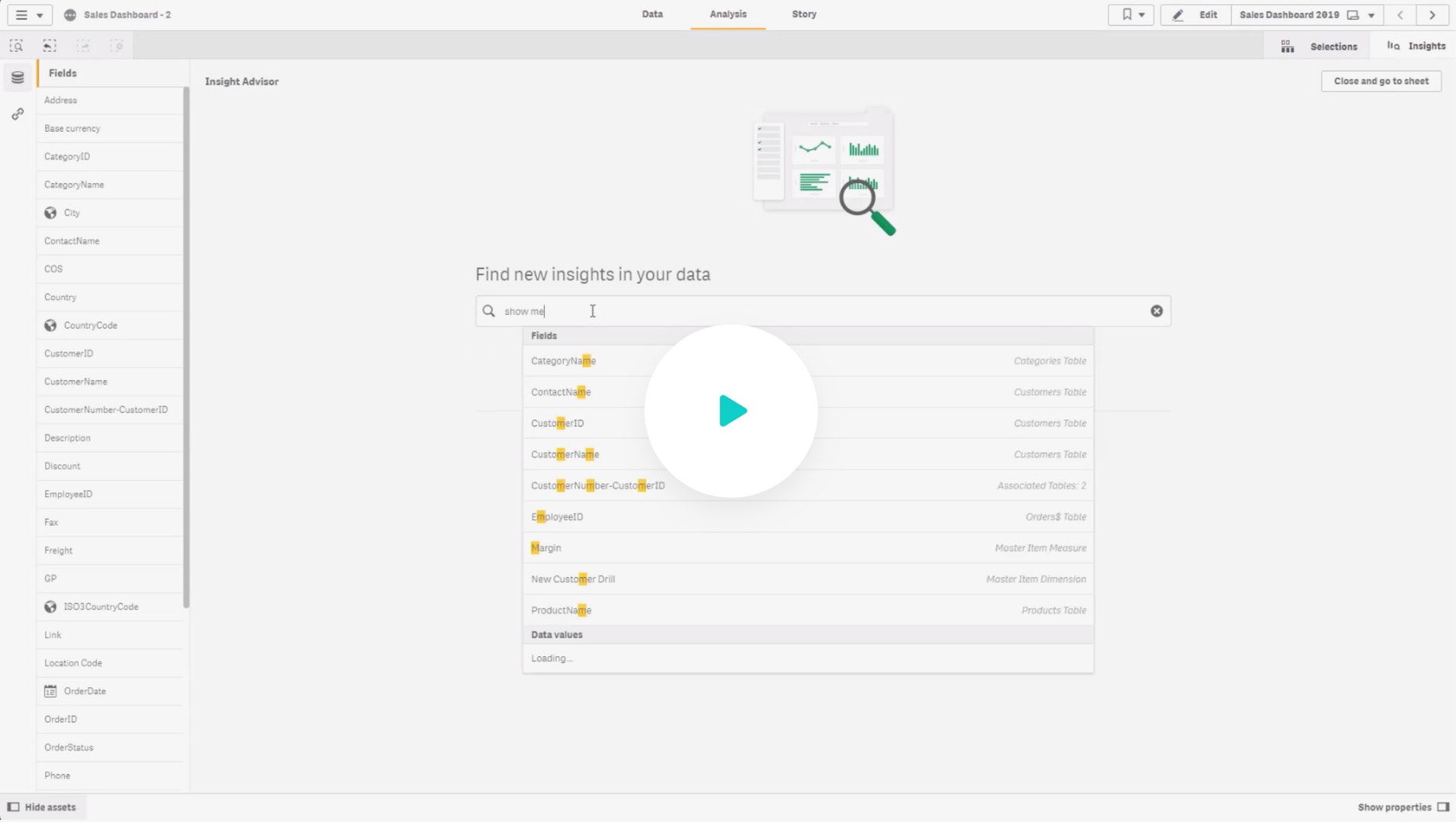
Big Data Analytics
What it is, why it matters and best practices. This guide provides a definition of big data analytics and how it works plus practical advice to help you succeed with big data and analytics in your organization.
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data analytics is the use of processes and technologies to combine and analyze massive datasets with the goal of identifying patterns and developing actionable insights. This helps business leaders make faster, better, data-driven decisions that can increase efficiency, revenue and profits.
How Big Data Analytics Works
The primary steps of big data analytics are goal definition, data collection, data integration and management, data analysis and sharing of findings. The advanced analytics involved in exploring and analyzing large volumes of semi-structured and unstructured data requires either an end-to-end big data analytics platform or a broad set of tools which are applied by data analysts, data scientists, or engineers.
Modern big data analytics involves the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to automate processes, provide insight suggestions, perform predictive analytics and allow natural language interaction. Real-time big data analytics involves processing data as it arrives, which can further speed decision making or trigger actions or notifications.
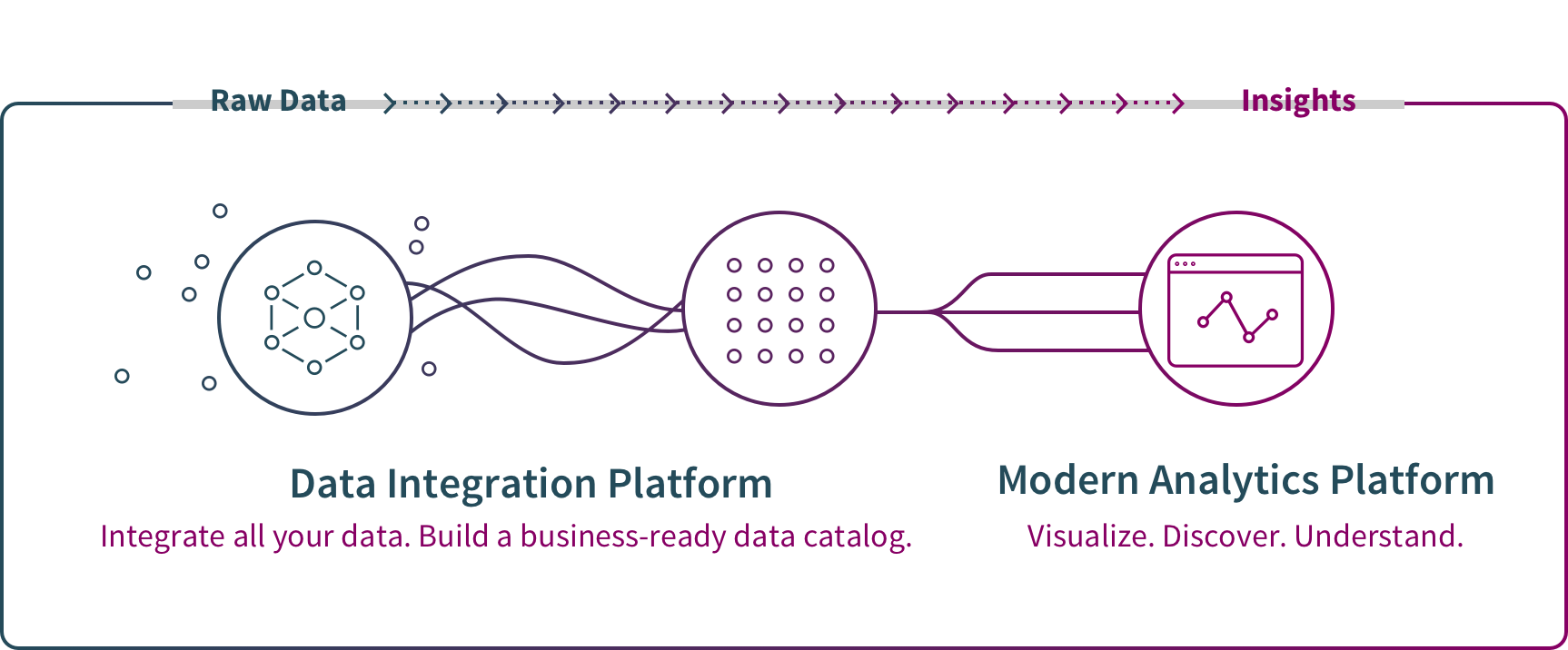
Now let’s get more specific.
Once the data has been collected and you’ve clearly defined your business objective (such as improving marketing ROI), below are the key steps and processes involved:
1. Big Data Integration & Management
Before conducting big data analytics, source data must be transformed into clean, business-ready information. Big data integration is the process of combining data from many sources across an organization to provide complete, accurate, and up-to-date information for big data analytics usage. As described below, big data replication, ingestion, consolidation and storage bring different types of data into standardized formats stored in a repository such as a data lake or data warehouse.

-
Big data replication
Big data analytics requires fast data access, high performance, and having an accurate backup of the data. To make this happen, the process of data replication copies data from master sources to one or more locations. This process can even happen in real time as data is written, changed, or deleted by using change data capture (CDC) technology. -
Big data ingestion
Raw data from a variety of sources needs to be moved to a storage location such as a data warehouse or data lake. This process, called big data ingestion, can be streamed in real time or in batches. Ingestion also usually includes cleaning and standardizing the data to make it ready for a big data analytics tool.
-
Big data consolidation and storage
For big data analytics, data is stored in a data lake or data warehouse. The Hadoop data lake open source software framework is now popular because the framework is free and its distributed computing model can quickly process big data. -
Governed big data
Big data analytics tools should also provide a governed enterprise data catalog. This allows IT to profile and document every data source and define who in the organization can take which actions on which data. This allows users to more easily find, use and share trusted data sets on their own.
2. Big Data Analysis
This step in the process involves exploring and analyzing the data and uncovering meaningful patterns, relationships and trends. The goals are to both answer specific questions and to discover new questions and gain unanticipated insights.
Here we briefly describe the key processes and technologies used in big data analysis.
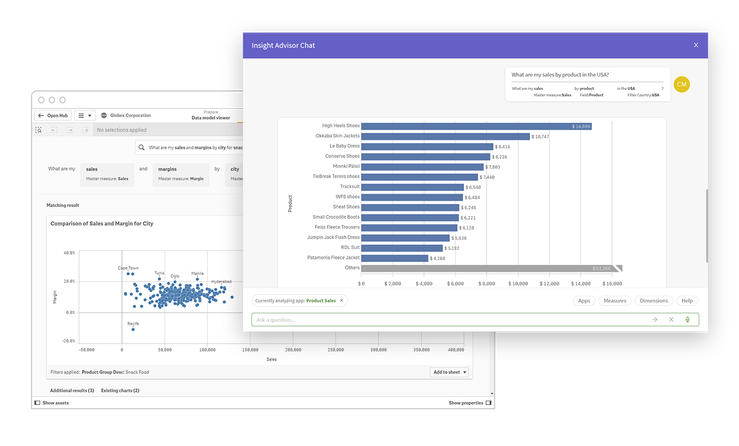
Conversational analytics, also powered by AI, lets users ask questions in natural language and have answers presented in an easy-to-understand conversational manner.
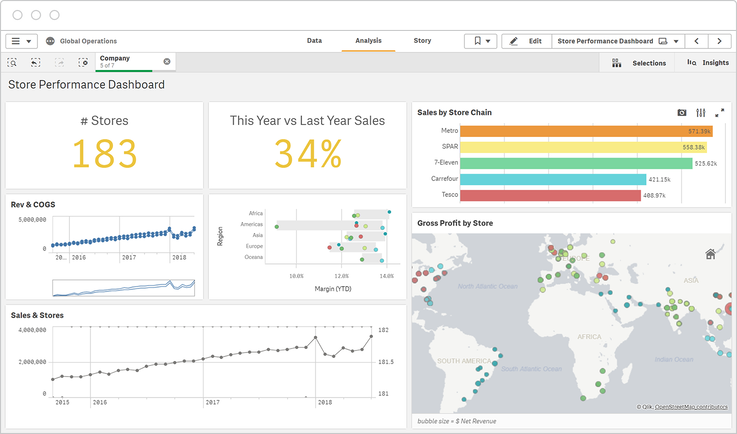
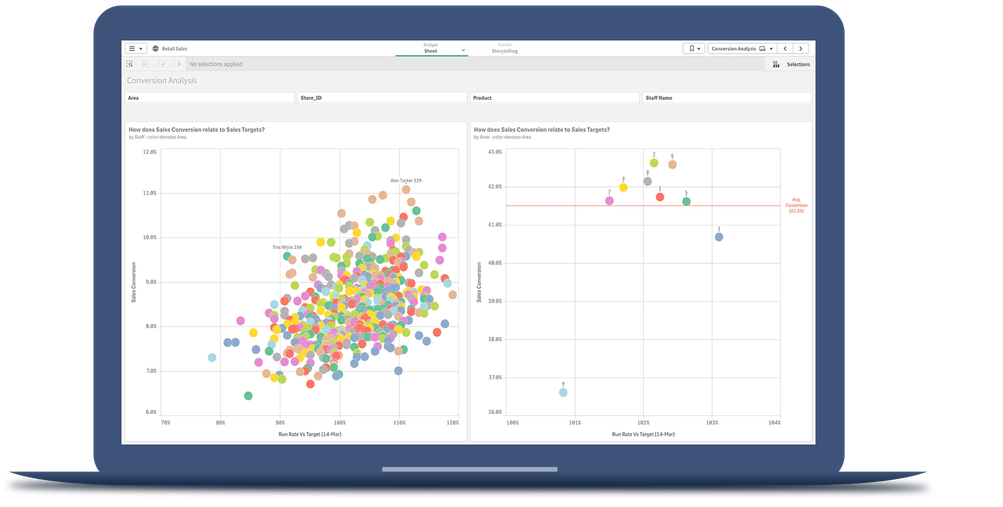
Big data visualization makes it easier for analysts and stakeholders to understand and engage with big data and share insights across an organization.
Predictive analytics
Data mining
Text mining
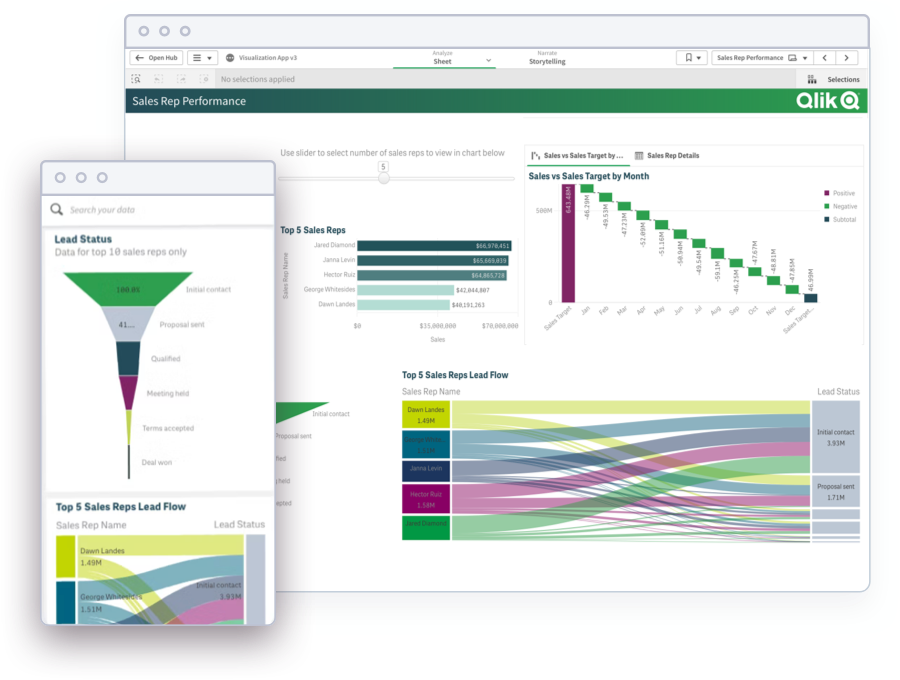
Modern Analytics Demo Videos
See how to explore information and quickly gain insights.
- Combine data from all your sources
- Dig into KPI visualizations and dashboards
- Get AI-generated insights
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big data analytics is too broad a discipline for one single tool to completely cover. Naturally, big data analytics software is the primary tool, but below we briefly describe the related supporting technologies in order of the overall process.
Big data replication and change data capture (CDC) tools copy data from master sources to other locations. As described above, these tools allow for fast data access, high performance, and an accurate backup of the data.
Big data ingestion tools move raw big data from a variety of sources to a storage location such as a data warehouse or data lake.
Big data consolidation and storage tools such as a Hadoop data lake, allow for big data analytics usage by making data available to be processed and used flexibly for deep analysis.
- As stated above, the Hadoop data lake framework is popular because the open source software framework is free and its distributed computing model can quickly process big data. There are two key components of the Hadoop framework. The first is MapReduce, which filters data to nodes of the cluster and reduces the results from each node for a given query. The second is a cluster management technology called YARN which assists with job scheduling and resource management across the cluster.
- A NoSQL database can also handle a variety of data models and is another good option for raw, unstructured big data. This is because its non-relational data management system doesn’t require a fixed scheme.
- In contrast, a data warehouse typically stores structured, filtered data that’s been processed for a specific purpose and is therefore not as popular for the often highly unstructured nature of big data. Learn more about data lake vs data warehouse.

An end-to-end self-service big data analytics tool, such as Qlik Sense, lets all users easily integrate, explore, and analyze big data without the need for writing code. The tool also makes it easy to collaborate and share insights across an organization through data visualization, interactive dashboards, embedded analytics and automated reports.
Here are three key big data-related capabilities to look for in a true end-to-end self-service big data analytics tool:
- Free Form Big Data Exploration. Your tool should allow anyone in your organization to act like a data scientist and freely explore their big data in any direction using an associative engine rather than a linear, query-based approach.
- Smart Big Data Pipelines. Modern big data analytics tools should also have data integration capabilities that automatically move, consolidate and transform big data from a variety of data sources while maintaining lineage.
- Open Platform. Third, your tool should have an open data integration platform and many out-of-the-box connectors. This will let you quickly integrate data from an ever-growing ecosystem of new technologies such as Hadoop, NoSQL, Databricks, Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery.
Compare top big data analytics tools Power Bi vs Tableau vs Qlik.
Big Data Analytics Benefits
The primary benefit of conducting big data analytics is finding actionable business insights that increase efficiency, revenue and profits. A business insight is a deep understanding on a particular issue a user gains from analyzing data. Insights are actionable if they’re specific and relevant enough to direct actions.
With the right tools and strategy, here are four key ways big data analytics can deliver value for your organization:
- Conduct faster, more accurate analysis, planning and business decisions
- Reduce expenses by optimizing business processes and performance
- Increase customer loyalty and lifetime value through a deeper understanding of customers and customer behavior
- Identify new markets and sources of revenue by analyzing market trends and purchase behavior
Big Data Analytics Challenges
Most organizations understand the potential that analyzing their big data presents. However, there can be considerable challenges in fully realizing this potential. Here are the key challenges:
- Integrating data from legacy systems and ensuring that information is accurate and in the proper format for analysis, i.e. analytics-ready.
- Maintaining data governance and quality of massive volumes of data from a variety of sources from across an organization can be a tall order.
- A lack of skilled data analysts, data scientists and engineers within the organization and the difficulty and expense associated with finding these resources. This is why modern self-service analytics solutions are gaining such traction.
- Low data literacy levels among senior management and the workforce in general.
- Concerns about data privacy and security. Now more than ever before, companies are under pressure to ensure that they are following industry standards and government requirements when collecting, handling, and storing consumer personal and sensitive data.
More Resources on Big Data Analytics
These resources provide our latest thinking on big data and analytics.